Page 90 -
P. 90
โครงการรวบรวมและจัดทําเอกสารวารสารอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ มหาวิทยาลัยเกษตรศาสตร์
79
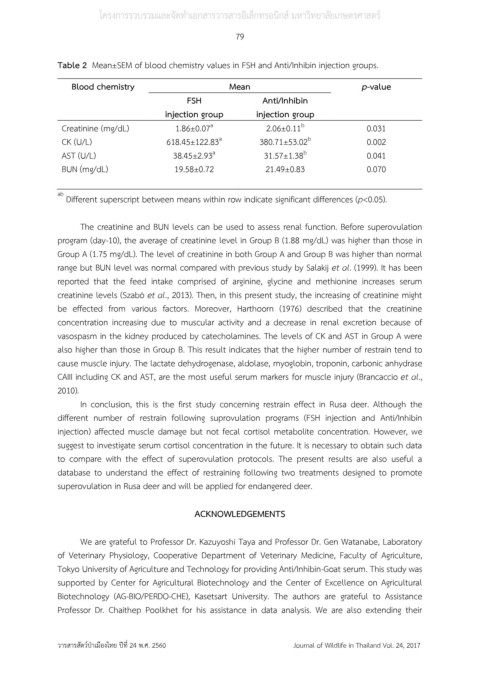
Table 2 Mean±SEM of blood chemistry values in FSH and Anti/Inhibin injection groups.
Blood chemistry Mean p-value
FSH Anti/Inhibin
injection group injection group
a
b
Creatinine (mg/dL) 1.86±0.07 2.06±0.11 0.031
a
b
CK (U/L) 618.45±122.83 380.71±53.02 0.002
a
AST (U/L) 38.45±2.93 31.57±1.38 0.041
b
BUN (mg/dL) 19.58±0.72 21.49±0.83 0.070
ab
Different superscript between means within row indicate significant differences (p<0.05).
The creatinine and BUN levels can be used to assess renal function. Before superovulation
program (day-10), the average of creatinine level in Group B (1.88 mg/dL) was higher than those in
Group A (1.75 mg/dL). The level of creatinine in both Group A and Group B was higher than normal
range but BUN level was normal compared with previous study by Salakij et al. (1999). It has been
reported that the feed intake comprised of arginine, glycine and methionine increases serum
creatinine levels (Szabó et al., 2013). Then, in this present study, the increasing of creatinine might
be effected from various factors. Moreover, Harthoorn (1976) described that the creatinine
concentration increasing due to muscular activity and a decrease in renal excretion because of
vasospasm in the kidney produced by catecholamines. The levels of CK and AST in Group A were
also higher than those in Group B. This result indicates that the higher number of restrain tend to
cause muscle injury. The lactate dehydrogenase, aldolase, myoglobin, troponin, carbonic anhydrase
CAIII including CK and AST, are the most useful serum markers for muscle injury (Brancaccio et al.,
2010).
In conclusion, this is the first study concerning restrain effect in Rusa deer. Although the
different number of restrain following suprovulation programs (FSH injection and Anti/Inhibin
injection) affected muscle damage but not fecal cortisol metabolite concentration. However, we
suggest to investigate serum cortisol concentration in the future. It is necessary to obtain such data
to compare with the effect of superovulation protocols. The present results are also useful a
database to understand the effect of restraining following two treatments designed to promote
superovulation in Rusa deer and will be applied for endangered deer.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Professor Dr. Kazuyoshi Taya and Professor Dr. Gen Watanabe, Laboratory
of Veterinary Physiology, Cooperative Department of Veterinary Medicine, Faculty of Agriculture,
Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology for providing Anti/Inhibin-Goat serum. This study was
supported by Center for Agricultural Biotechnology and the Center of Excellence on Agricultural
Biotechnology (AG-BIO/PERDO-CHE), Kasetsart University. The authors are grateful to Assistance
Professor Dr. Chaithep Poolkhet for his assistance in data analysis. We are also extending their
วารสารสัตว์ป่าเมืองไทย ปีที่ 24 พ.ศ. 2560 Journal of Wildlife in Thailand Vol. 24, 2017