Page 85 -
P. 85
ิ
ิ
์
โครงการหนังสออเล็กทรอนกสด้านการเกษตร เฉลมพระเกียรตพระบาทสมเด็จพระเจ้าอยู่หัว
ิ
ิ
ื
TEAK IN MEKONG
The main known sources of plantation Several of these species are promoted
grown wood are smallholder teak for planting during National Arbor Day but
plantations (Tectona grandis; ‘mai sak’) and precise records of actual planting and
Eucalyptus and Acacia from largely survival are not kept.
investor owned/managed plantations. Rubber is established principally for latex,
Other species grown in plantations and there is currently no formal value chain
such Agarwood (Aquilaria crassna; ‘mai for rubber wood in Lao PDR, although
ketsana’), Benzoin (Styrax tonkinensis, anecdotally rubber wood logs are being
‘mai nyarn’) and Yang (Nothalphoebe exported to China from northern Lao PDR,
umbellifiora, ‘mai bong’) are not typically where plantations are being harvested due
grown for timber products, but rather are to low latex prices. Around 54,000 ha of
harvested for aromatic wood, resin or bark new plantations are needed to be
for processing into incense or oil. Pink established between 2016 and 2020 to reach
Mampat (Cratoxylum formosum and the 500,000-ha target.
Cratexylon prunitfolium, ‘mai tiew’) is
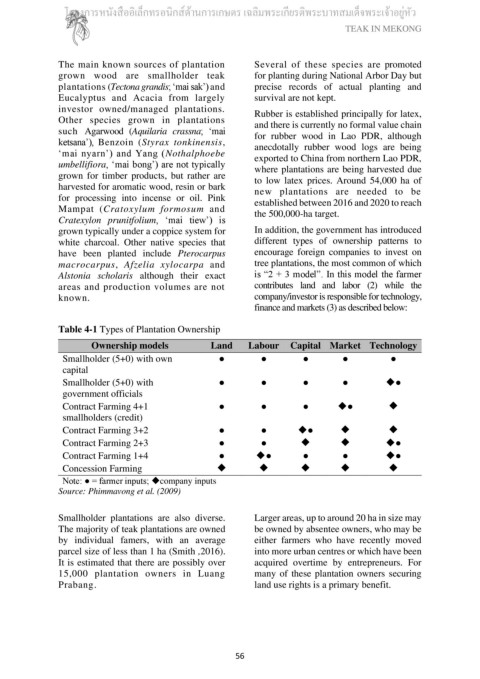
grown typically under a coppice system for In addition, the government has introduced
white charcoal. Other native species that different types of ownership patterns to
have been planted include Pterocarpus encourage foreign companies to invest on
macrocarpus, Afzelia xylocarpa and tree plantations, the most common of which
Alstonia scholaris although their exact is “2 + 3 model”. In this model the farmer
areas and production volumes are not contributes land and labor (2) while the
known. company/investor is responsible for technology,
finance and markets (3) as described below:
Table 4-1 Types of Plantation Ownership
Ownership models Land Labour Capital Market Technology
Smallholder (5+0) with own ● ● ● ● ●
capital
Smallholder (5+0) with ● ● ● ● ◆●
government officials
Contract Farming 4+1 ● ● ● ◆● ◆
smallholders (credit)
Contract Farming 3+2 ● ● ◆● ◆ ◆
Contract Farming 2+3 ● ● ◆ ◆ ◆●
Contract Farming 1+4 ● ◆● ● ● ◆●
Concession Farming ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆
Note: ● = farmer inputs; ◆company inputs
Source: Phimmavong et al. (2009)
Smallholder plantations are also diverse. Larger areas, up to around 20 ha in size may
The majority of teak plantations are owned be owned by absentee owners, who may be
by individual famers, with an average either farmers who have recently moved
parcel size of less than 1 ha (Smith ,2016). into more urban centres or which have been
It is estimated that there are possibly over acquired overtime by entrepreneurs. For
15,000 plantation owners in Luang many of these plantation owners securing
Prabang. land use rights is a primary benefit.
56